Knee Arthroscopy
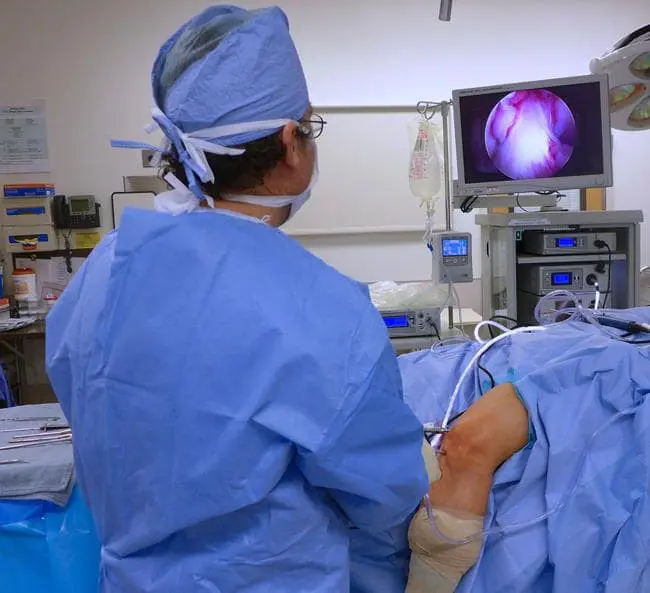
Knee arthroscopy is a surgical procedure that allows doctors to view the knee joint without making a large incision (cut) through the skin and other soft tissues. Arthroscopy is used to diagnose and treat a wide range of knee problems.
Because the arthroscope and surgical instruments are thin, your surgeon can use very small incisions, rather than the larger incision needed for open surgery. This results in less pain and joint stiffness for patients, and often shortens the time it takes to recover and return to favorite activities.
Anatomy
Other important structures that make up the knee joint include:
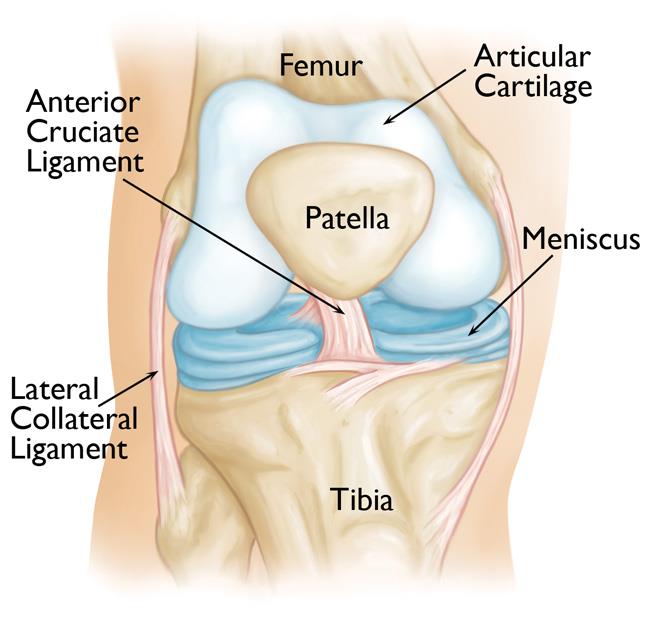
- Articular cartilage. The ends of the femur and tibia, and the back of the patella are covered with articular cartilage. This slippery substance helps your knee bones glide smoothly across each other as you bend or straighten your leg.
- Synovium. The knee joint is surrounded by a thin lining called synovium. This lining releases a fluid that lubricates the cartilage and reduces friction during movement.
- Meniscus. Two wedge-shaped pieces of meniscal cartilage between the femur and tibia act as shock absorbers. Different from articular cartilage, the meniscus is tough and rubbery to help cushion and stabilize the joint.
- Ligaments. Bones are connected to other bones by ligaments. The four main ligaments in your knee act like strong ropes to hold the bones together and keep your knee stable.
- The two collateral ligaments are found on either side of your knee.
- The two cruciate ligaments are found inside your knee joint. They cross each other to form an X with the anterior cruciate ligament in front and the posterior cruciate ligament in back.
Normal anatomy of the knee. Arthroscopy is commonly used to diagnose and treat problems that damage the articular cartilage, ligaments, and other structures around the joint.
When Knee Arthroscopy is Recommended
Your doctor may recommend knee arthroscopy if you have a painful condition that does not respond to nonsurgical treatment. Nonsurgical treatment includes rest, physical therapy, and medications or injections that can reduce inflammation.
Knee arthroscopy may relieve painful symptoms of many problems that damage the cartilage surfaces and other soft tissues surrounding the joint.
Common arthroscopic procedures for the knee include:
- Partial meniscectomy (removal of the meniscus), repair of a torn meniscus, or meniscus transplantation
- Reconstruction of a torn anterior cruciate ligament or posterior cruciate ligament
- Removal of inflamed synovial tissue
- Trimming or reconstruction of damaged articular cartilage
- Removal of loose fragments of bone or cartilage, like those caused by synovial chondromatosis
- Treatment of patella (kneecap) problems
- Treatment of knee sepsis (infection)
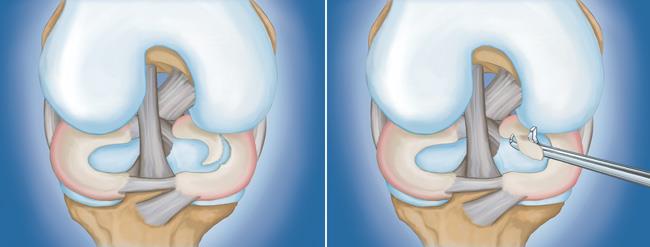
(Right) Arthroscopic removal of the damaged meniscal tissue.
Preparing for Surgery
Evaluations and Tests
Your orthopaedic surgeon may recommend that you see your primary doctor to assess your general health before your surgery. They will identify any problems that may interfere with the procedure. If you have certain health risks, a more extensive evaluation may be necessary before your surgery.
To help plan your procedure, your orthopaedic surgeon may order preoperative tests. These may include blood tests or an electrocardiogram (EKG).
Admissions Instructions
If you are generally healthy, your knee arthroscopy will most likely be performed as an outpatient procedure. This means you will not need to stay overnight at the hospital.
Be sure to inform your orthopaedic surgeon of any medications or supplements that you take. You may need to stop taking some of these before surgery.
The hospital or surgery center will contact you ahead of time to provide specific details about your procedure. Make sure to follow the instructions on when to arrive and especially on when to stop eating or drinking prior to your procedure.
Anesthesia
Before your surgery, a member of the anesthesia team will talk with you. Knee arthroscopy can be performed under local, regional, or general anesthesia:
- Local anesthesia numbs just your knee
- Regional anesthesia numbs you below the waist
- General anesthesia puts you to sleep
Your orthopaedic surgeon and your anesthesiologist will talk to you about which method is best for you.
Surgical Procedure
Positioning
Once you are moved into the operating room, you will be given anesthesia. To help prevent surgical site infection, the skin on your knee will be cleaned. Your leg will be covered with surgical draping that exposes the prepared incision site.
At this point, a positioning device is sometimes placed on the leg to help stabilize the knee while the arthroscopic procedure takes place.
Procedure
To begin the procedure, the surgeon will make a few small incisions, called portals, in your knee. A sterile solution will be used to fill the knee joint and rinse away any cloudy fluid. This helps your orthopaedic surgeon see the structures inside your knee clearly and in great detail.
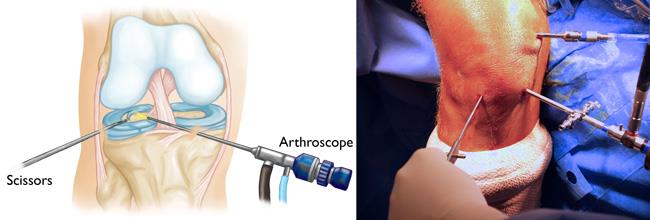
Specialized instruments are used for tasks like shaving, cutting, grasping, and meniscal repair. In many cases, special devices are used to anchor stitches into bone.
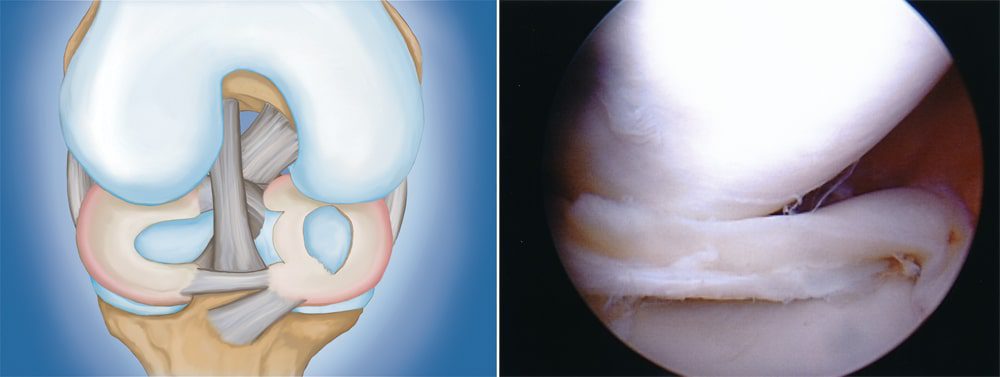
(Right) A photo of a bucket handle tear taken through an arthroscope.
Closure
Most knee arthroscopy procedures last less than an hour. The length of the surgery will depend upon the findings and the treatment necessary.
Your surgeon may close each incision with a stitch or steri-strips (small adhesive strips), then wrap your knee with a soft bandage. Sometimes braces are used post-operatively if a repair or reconstruction is performed that must be protected.
Complications
- Infection
- Blood clots
- Knee stiffness
- Accumulation of blood in the knee
- Bruising or swelling
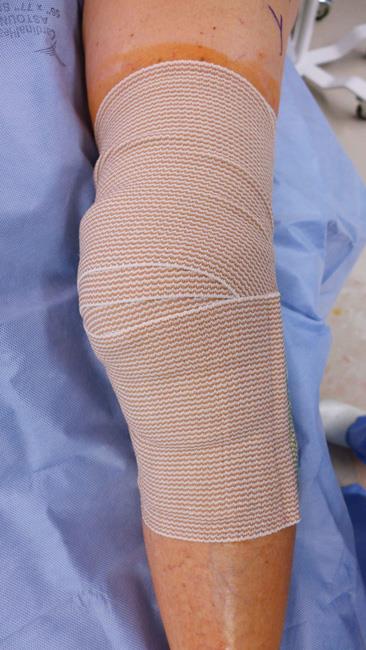
Recovery
After surgery, you will be moved to the recovery room and should be able to go home within 1 or 2 hours. Be sure to have someone with you to drive you home and check on you that first evening.
While recovery from knee arthroscopy is faster than recovery from traditional open knee surgery, it is important to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully after you return home.
Pain Management
After surgery, you will feel some pain. This is a natural part of the healing process. Your doctor and nurses will work to reduce your pain, which can help you recover from surgery faster.
Medications are often prescribed for short-term pain relief after surgery. Many types of medicines are available to help manage pain, including opioids, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and local anesthetics. Your doctor may use a combination of these medications to improve pain relief, as well as minimize the need for opioids.
Be aware that although opioids help relieve pain after surgery, they are a narcotic and can be addictive. Opioid dependency and overdose has become a critical public health issue in the U.S. It is important to use opioids only as directed by your doctor and to stop taking them as your pain begins to improve. Talk to your doctor if your pain has not begun to improve within a few days of your surgery.
Medications
In addition to medicines for pain relief, your doctor may recommend medication such as aspirin to lessen the risk of blood clots.
Swelling
Keep your leg elevated as much as possible for the first few days after surgery. Apply ice as recommended by your doctor to relieve swelling and pain. Your weight-bearing status after surgery will be dictated by what is performed during the surgery.
Dressing Care
You will leave the surgical facility with a dressing covering your knee. Keep your incisions clean and dry. Your surgeon will tell you when you can shower or bathe, and when you should change the dressing.
You will be seen in the office after surgery to check your progress, review the surgical findings, and begin your postoperative treatment program.
Bearing Weight
Most patients do not need crutches or other assistance after arthroscopic surgery. Your surgeon will tell you when it is safe to put weight on your foot and leg. If you have any questions about bearing weight, call your surgeon.
Rehabilitation Exercise
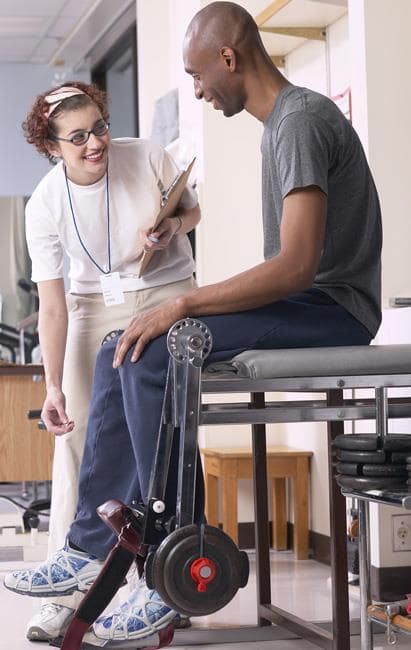
You should exercise your knee regularly for several weeks after surgery. This will restore motion and strengthen the muscles of your leg and knee.
Therapeutic exercise will play an important role in how well you recover. A formal physical therapy program may improve your final result.
Driving
Typically, patients are able to drive from 1 to 3 days after surgery if the procedure was minor. More time may be needed for more extensive repairs or reconstructions.

Outcome
Unless you have had a ligament reconstruction, meniscus repair, or cartilage restoration, you should be able to return to most physical activities after 6 to 8 weeks, or sometimes much sooner. You may, however, need to avoid higher impact activities for a longer time.
If your job involves heavy work, it may be longer before you can return to your job. Discuss with your doctor when you can safely return to work.
For some people, lifestyle changes are necessary to protect the joint. An example might be changing from high impact exercise (such as running) to lower impact activities (such as swimming or cycling). These are decisions you will make with the guidance of your surgeon.
Sometimes, the damage to your knee can be significant enough that it cannot be completely reversed with arthroscopic surgery. More extensive operations may be needed in the future for these more severe conditions.